快速排序的算法的性能取决于划分的对称性。通过修改函数 Partition ,可以设计出采用随机选择策略的快速排序算法。在快速排序算法的每一步中,当数组还没有被划分时,可以在 a[p:r] 中随机选出一个元素作为划分基准,这样可以使划分基准的选择是随机的,从而可以期望划分是较对称的。
代码如下:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- int a[]={15,56,2,51,1,59,3}; // 待排序数组 a
-
- void Swap( int *a, int *b) { // 函数 Swap 实现两数的对调操作
- int temp;
- temp=*a;*a=*b;*b=temp;
- }
-
- int Random(int p,int r) { // 产生 p 和 r 之间的一个随机整数
- int result=p+rand()%(r-p+1);
- return result;
- }
-
- int Partition( int a[], int p, int r) {
- int i=p,j=r+1; int x=a[p];
- // 将 <x 的元素交换到左边区域
- // 将 >x 的元素交换到右边区域
- while ( true ) {
- while (a[++i]<x&&i<=r); while (a[--j]>x&&j>=p);
- if (i>=j) break ;
- Swap (&a[i],&a[j]);
- }
- a[p]=a[j]; a[j]=x; return j;
- }
-
- int RandomizedPartition( int a[], int p, int r) {
- int i=Random(p,r);
- Swap (&a[i],&a[p]);
- return Partition(a,p,r);
- }
-
- void RandomizedQuickSort( int a[], int p, int r) {
- if (p<r) {
- int q= RandomizedPartition (a,p,r);
- RandomizedQuickSort (a,p,q-1); RandomizedQuickSort(a,q+1,r);
- }
- }
-
- void main() {
- for ( int i=0;i<7;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]);
- printf ("\n");
- RandomizedQuickSort (a,0,6);
- for (i=0;i<7;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]);
- printf ("\n");
- }
其中,函数 Random(p,r) 产生 p 和 r 之间的一个随机整数,且产生不同整数的概率相同。随机化的快速排序算法通过调用 RandomizedPartition 来产生随机的划分。
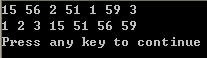
程序效果:
 作者:w397090770 发表于2011-12-19 22:09:34 原文链接 作者:w397090770 发表于2011-12-19 22:09:34 原文链接 |